1 中北大学 南通智能光机电研究院, 江苏 南通 226000
2 中北大学 仪器与电子学院, 山西 太原 030051
随着精密机械制造、高性能半导体器件加工等领域对位移检测要求的不断提高, 对于高性能微型位移传感器件的需求日益迫切。基于微纳光栅光学自成像效应, 提出了一种双光栅结构的光学位移检测方法。研究了~6.5μm周期微纳光栅的光强空间分布, 分析了双光栅结构光强透过特性, 并在实验中实现了1mm位移范围内的正弦信号输出。通过对输出信号进行100倍电学细分, 最终实现灵敏度为64.5nm的位移检测。所提方法具有光路简单、结构紧凑、稳定性高的特点, 可用于集成化高性能微位移传感器件与系统等应用。
微纳光栅 自成像效应 光学干涉 位移检测 光学传感 optical micrograting Self-imaging effect optical interference displacement measuring optical sensing
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, China
2 School of Instrument and Electronics, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
4 School of Information and Communication Engineering, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, China
Based on the transverse second-harmonic generation (TSHG) effect, we demonstrate a method for in-situ modal inspection of nonlinear micro/nanowaveguides. Pumping lights are equally split and coupled into two ends of a single CdS nanobelt (NB). As pumping light counter-propagates along the NB, transverse second-harmonic (TSH) interference patterns are observed. The influence of multimode interaction on the TSHG effect is discussed in detail. Using fast Fourier transform, TSH interference patterns are analyzed, indicating the existence of at least four modes inside the NB. Experimental beat lengths are found to be in agreement with calculated results.
micro/nanowaveguides transverse second-harmonic generation multimode interference modal inspection Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(7): 071901
1 中北大学前沿交叉科学研究院, 山西 太原 030051
2 中北大学电子测试技术国防重点实验室, 山西 太原 030051
3 中北大学山西省光电信息与仪器工程技术研究中心, 山西 太原 030051
利用波片进行同步相位延迟,将波片与偏振分光棱镜相结合获得四路相位差为90°的正弦信号,从而将衍射光栅位移传感器的量程范围提升到激光相干长度的二分之一。对两路相位差为180°的信号进行差分处理,可有效避免激光功率抖动、背景光干扰、运放温度漂移等因素带来的影响。最后利用细分插值电路对光路的输出信号构建反正切函数,实现了正弦函数的非线性模/数转换及2.54 nm的位移分辨率。这种具有高分辨率、大量程的位移传感器未来将进一步推动自动化机械设备、电子制造业以及工业智能领域的快速发展。
光栅 位移检测 分辨率 光学传感与传感器

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
2 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
4 e-mail: phytong@zju.edu.cn
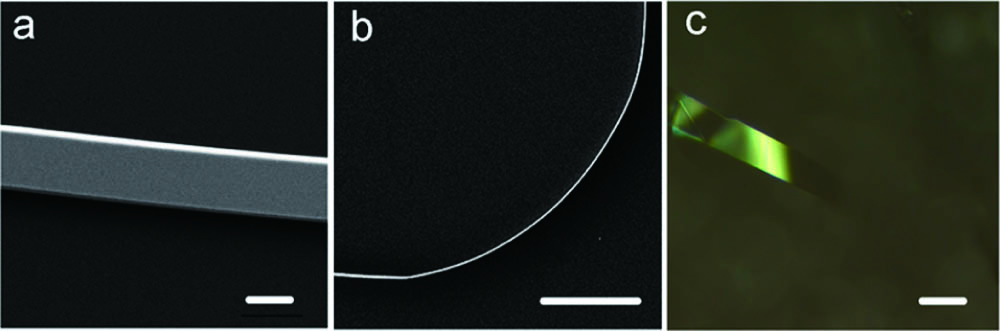
A novel type of mid-IR microresonator, the chalcogenide glass (ChG) microfiber knot resonator (MKR), is demonstrated, showing easy fabrication, fiber-compatible features, resonance tunability, and high robustness. ChG microfibers with typical diameters around 3 μm are taper-drawn from glass fibers and assembled into MKRs in liquid without surface damage. The measured factor of a typical 824 μm diameter ChG MKR is about at the wavelength of 4469.14 nm. The free spectral range (FSR) of the MKR can be tuned from 2.0 nm (28.4 GHz) to 9.6 nm (135.9 GHz) by tightening the knot structure in liquid. Benefitting from the high thermal expansion coefficient of glass, the MKR exhibits a thermal tuning rate of at the resonance peak. When embedded in polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) film, a 551 μm diameter MKR retains a factor of . The ChG MKRs demonstrated here are highly promising for resonator-based optical technologies and applications in the mid-IR spectral range.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(4): 04000616





